
loading
Embraer is the result of the work of thousands of people who, throughout 47 years, have taken on the challenge of establishing a Brazilian company as one of the main forces in the global aerospace market.
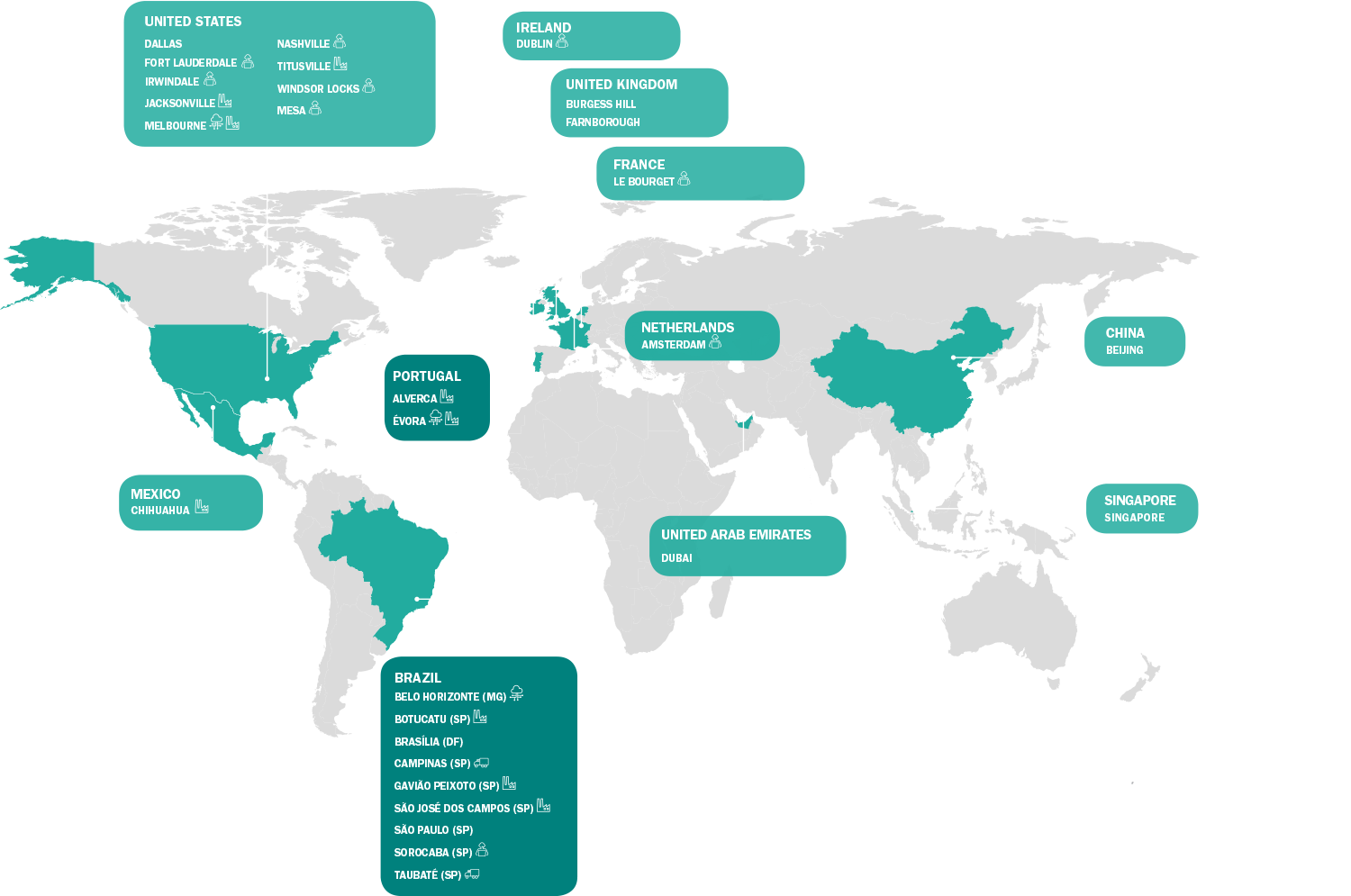
Founded in 1969, the company started operations in São José dos Campos, Brazil, its headquarters to this day, with current presence in 10 Brazilian cities and 17 more cities abroad. The company also holds 51% of the shares of Visiona Tecnologia Espacial Telebras, a joint venture with Telebras; and 65% of the Portuguese company OGMA, which specializes in aircraft maintenance and manufacturing. Comprising the holding structure are also the companies ELEB, Embraer Aero Seating Technologies (EAST), Atech, Savis and Bradar. G4-5, G4-6, G4-8, G4-9
With cutting-edge technology and human resources, the company designs, develops, manufactures and sells aircraft, systems and solutions for the Commercial Aviation, Executive Aviation and Defense & Security segment (see Customers), offering customer support and services in over 100 countries. G4-4
Embraer ended the fiscal year with 18,506 employees throughout the world and delivered 240 aircraft, recording US$6.2 billion in net income and US$19.6 billion in firm orders. G4-9
 EVERY 10 SECONDS, AN EMBRAER AIRCRAFT TAKES OFF SOMEWHERE IN THE WORLD
EVERY 10 SECONDS, AN EMBRAER AIRCRAFT TAKES OFF SOMEWHERE IN THE WORLD  GLOBAL LEADER IN COMMERCIAL JETS WITH UP TO 130 SEATS
GLOBAL LEADER IN COMMERCIAL JETS WITH UP TO 130 SEATS
OUR PEOPLE ARE WHAT MAKE US FLY | Our people are happy, competent, valued, fulfilled, and committed to what they do. People who work as teams and who act with integrity, coherence, trust in each other and respect for diversity.
WE ARE HERE TO SERVE OUR CUSTOMERS | Customer loyalty is earned by ensuring their total satisfaction and by building strong and enduring relationships. Partnerships are established based on real commitment and flexibility.
WE STRIVE FOR COMPANY EXCELLENCE | Company actions are aimed at simplicity, agility, flexibility and safety, while constantly striving for improvement and excellence. An entrepreneurial attitude is built on integrated planning, responsible delegation and disciplined execution.
BOLDNESS AND INNOVATION ARE OUR HALLMARKS | Company on the technological forefront, with a capacity for continuous learning; internal transformation and influencing the markets of its businesses. A strategic vision and an ability to overcome challenges with creativity and courage.
GLOBAL PRESENCE IS OUR FRONTIER | We demonstrate a global presence and mindset, acting locally to leverage competitiveness and using the best of each location, envisioning a world without borders, one that values diversity.
WE BUILD A SUSTAINABLE FUTURE | We are constantly striving to build the foundation for the company’s longevity, considering stockholders’ profitability, respect for quality of life, environment and society.
Embraer will further consolidate its position as one of the leading forces in the global aerospace and defense and security industries. Embraer is a market leader in the segments in which it operates and commands a reputation for excellence.
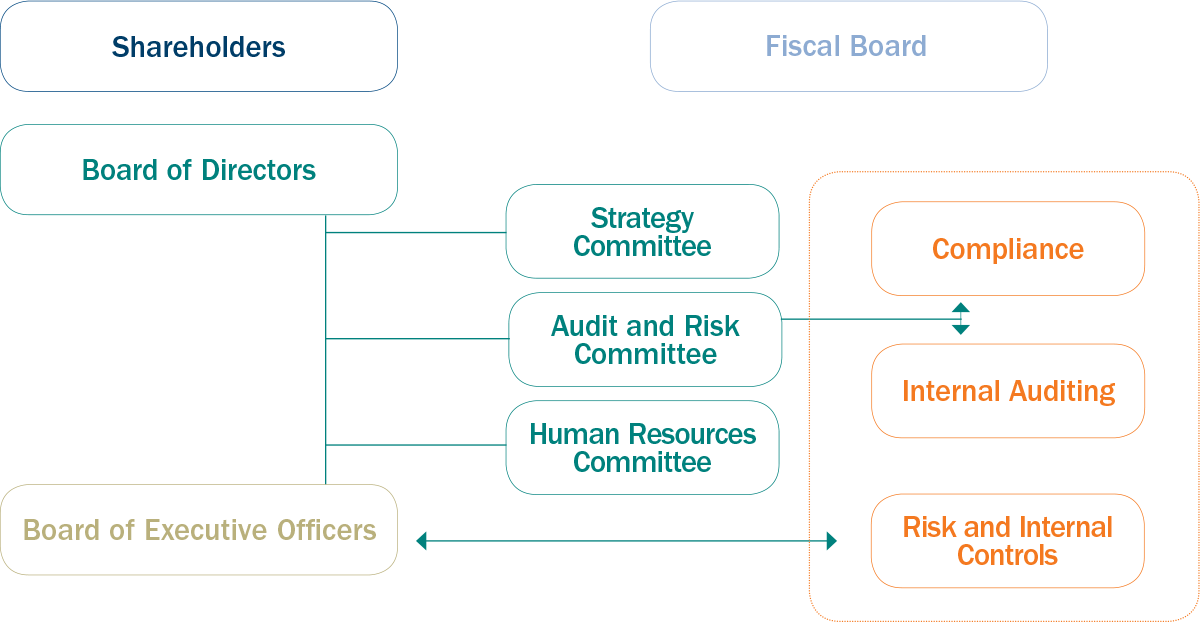
Embraer has adopted the most strict standards of corporate governance and is associated with the Brazilian Institute of Corporate Governance (IBGC, in Portuguese), the Brazilian Association of Public Companies (ABRASCA, in Portuguese), Brazilian Institute of Investor Relations (IBRI, in Portuguese) and the National Institute of Investors (INI, in Portuguese). In 2016, the company was listed on the DJSI for the seventh consecutive year, with three years of continual growth in its overall score. The company also comprises the ISE and the theoretical portfolios of the Brazil Index (IBrX, in Portuguese), the Corporate Governance Stock Index (IGC, in Portuguese), the Stock Index with Differentiated Tag Along (ITAG, in Portuguese), the Industrial Sector Index (INDX, in Portuguese), the Bovespa Index Value 2nd Line (IVBX 2, in Portuguese) and the Brazil Index 50 (IBrX 50, in Portuguese).
The company’s shares are listed in São Paulo on the New Market (BM&FBOVESPA: EMBR3) and in New York, on the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE: ERJ), through the American Depositary Receipts (ADRs) program, level III. In addition to the New Market requirements, the company’s bylaws impose onerous conditions on any shareholder who might hold shares equal or superior to 35% of the capital, including submission to Public Tender Offer (OPA, in Portuguese) as well as an authorization from the Brazilian government, holder of a special class share, which grants a veto right in some strategic matters for the company and the Country. G4-41

Michael Amalfitano, José Antonio de Almeida Filippo, John Stephen Slattery, Paulo Cesar de Souza e Silva, Jackson Medeiros de Faria Schneider, Fabiana Klajner Leschziner, Mauro Kern Junior, Mauricio Rodrigues Aveiro, Johann Christian Jean Charles Bordais and Nelson Krahenbuhl Salgado (absent)
The Compliance Program aims to ensure the adoption of the highest standards of integrity and international good practices as well as the adherence to the laws of the countries in which Embraer is present, above all those that govern anti-corruption practices and export control. The initiative is coordinated by the department of Compliance and supervised by the Board of Directors, the Audit and Risk Committee, and by the President and CEO.
During the fiscal year, the program intensified its relationship with the group of more than 200 compliance agents – employees from various departments, in Brazil and abroad – who act as multipliers of the culture of ethics and compliance in the company. Workshops were also held to ensure full comprehension of the company’s policies and how to execute them during daily tasks. The training plan includes lectures on ethics and integrity administered by Marjorie Doyle, member of the Society of Corporate Compliance and Ethics (SCCE).
Lectures were attended by more than 500 employees from several departments and by members of the Board of Directors.
Among the advances in the Compliance Program, we highlight the development of the Know Your Customer procedure, which requires a reputational analysis of potential clients based on risk factors, and the adoption of a continuous audit system that performs monitoring of critical operations, such as supplier payments, travel expenses, donations and sponsorships. The intention is to expand the system, which already serves the Internal Audit area, to other processes in the coming years.
In 2010, when potential nonconformities in certain overseas business transactions were questioned by U.S. authorities, the company hired external lawyers to conduct independent investigations, proactively expanding the initial scope and sharing the findings with the competent authorities. These investigations found that the company was responsible for irregular actions in four transactions involving 16 aircraft between 2007 and 2011 in Saudi Arabia, India, Mozambique and the Dominican Republic. On October 24, 2016, Embraer announced the terms for closing this case, which had been investigated by U.S. authorities – the United States Department of Justice (DOJ) and the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) – and by Brazilian authorities – Federal Public Prosecutor (MPF) and the Securities and Exchange Commission (CVM). As part of the agreements, the company agreed to contract external and independent monitoring for three years to monitor compliance with the terms and will make a payment of US$205.5 million to U.S. and Brazilian authorities. Upon timely fulfilment of the agreements, no charges will be brought against Embraer (see more information in the GRI Indicators).
The Anti-Corruption Policy and the Code of Ethics and Conduct ensure the company’s integrity in all operations. The former establishes guidelines to prevent conflicts of interest, deal with donations and sponsorships, the offering and receiving of gifts, and outsourcing. It also establishes mechanisms for investigations to be carried out prior to the formation of company partnerships.
The Code of Ethics and Conduct shares norms for responsible business management in all operations. The document is guided by internal business values and by the Global Compact of the United Nations, in addition to complying with anti-corruption laws, international trade, and initiatives such as the International Forum on Business Ethical Conduct (IFBEC) and the Partnering Against Corruption Initiative of the World Economic Forum (PACI-WEF). In 2016, the Board of Directors approved a revision regarding the prohibition of contributions to political parties.
The Code is available at http://compliance.embraer.com.br/en/SitePages/Home.aspx and all board members, members of the Board of Executive Officers, employees and third-party collaborators are trained in the document’s guidelines.
The Helpline is a tool to register allegations and concerns related to attitudes that violate the Code of Ethics and Conduct and the law. Contacts are consolidated by an independent company and forwarded to the Compliance department, in order to assure the confidentiality2 of the person who files the case, who also receives a protocol number to monitor its progress online.
Among the issues raised throughout 2016, nearly 60% were related to conduct deviation, of which 45% were pertinent. Referrals and solutions to the issues included coaching and conduct monitoring, in addition to disciplinary measures, such as warnings, suspensions and dismissals. G4-LA16, G4-HR12
In total, 325 reports were filed during the year, a 7% increase over 2015. This rise demonstrates the growing credibility of the channel and of the awareness among employees and third-party collaborators regarding the conduct expected by the company. In 2017, the Helpline changed its name to Helpline – Whistleblowing Channel, in order to help the public better understand its purpose.

Embraer’s risk management methodology is backed by the Risk Management Policy and is segmented into four categories in the figure below. This structure enables the concentration of efforts for more assertive monitoring, identification and mitigation, in each situation.
Upper management relies on the support of the Risk and Internal Controls department and is also involved, through interviews and meetings, in the periodic revision of trends and adversities that might compromise operational performance. The structure is reinforced by the Audit and Risk Committee, which ensures autonomy to the Internal Audit area as well as to the external audit services.
Employees, partners and suppliers may contact the following telephone numbers:
Brazil: 0800-721-5968
Portugal: 800-180-118
United States: 1-877-900-8779
Singapore: 800-130-2122
France: 0805-080608
China: 400-120-4946
Netherlands: 0800-450-0019
or on the site www.embraerhelpline.com
Risks that could impact the economic value of the brand and the image of embraer, which are related to decisions from the board of executive officers.
Resulting from failures or inadequacies in internal processes that result in loss of production, assets, customers or revenues. Also includes external events, such as natural catastrophes and other events resulting from climate change.
Risks related to exposure of financial operations. The company adopts protective measures aimed at increasing the generation of operating cash flow, the positive returns on financial transactions as well as fundraising. The company’s operations follow guidelines of the financial management policies approved by the board of directors.
Refers to compliance with local law where embraer operates, including regulations of the aeronautical sector at each stage of aircraft manufacturing, from design to post-sales support.
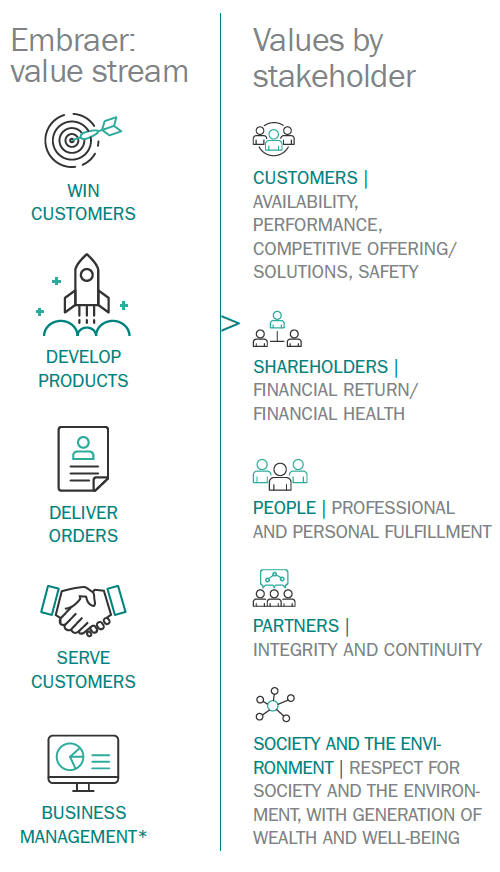
* In 2016, the company established the Business management value stream, which joined the previous flows Serving shareholders, Generating value for partners, Respecting society and the environment and Attracting and retaining people.
With respect to climate change, Embraer carries out risk analyses for periods of five years, considering aspects such as environmental laws (Brazilian laws and of countries in which Embraer operates), discussions on carbon taxation and the European Union Emissions Trading Scheme (EU ETS). The most recent analysis, carried out in 2012, did not identify any vulnerabilities of the company to these changes. The main factories are located in Brazil, a country that is not prone to extreme natural phenomena, and the units abroad are also at a low risk. Nevertheless, all operations follow guidelines to minimize adverse effects. In addition to categorizing risks considered to be environmental catastrophes, Embraer monitors potential impacts to its operations. Most of the units are ISO 14001 certified and the company maintains its goal of implementation of this certification at 100% of its manufacturing plants and service centers. G4-EC2
Embraer establishes a corporate procedure for identifying relationship guidelines related to each stakeholder. Based on the Principles of Excellence in Management and on the Model of Management Excellence (MEG, in Portuguese) from the National Quality Foundation (FNQ, in Portuguese), Embraer keeps the Embraer Business System (SEE, in Portuguese), which defines the main guidelines for the company’s business model. By presenting a systematic vision of Embraer, the SEE makes it possible to understand the main objectives of management by value streams, stimulating continuous improvement with focus on the stakeholders (customers, shareholders, people, partners, society and the environment), ensuring that all activities result in shared values (see more information in the GRI Indicators). G4-24, G4-25, G4-26
One of the fundamental elements of the company’s management model is the Embraer Enterprise Excellence Program (P3E), through which employees are engaged in re-envisioning processes for continual improvement of results. Divided into four pillars, the program is considered a key element for the evolution of corporate management.
The application of the lean management philosophy is the essence of P3E. Guided by the optimization of processes and the reduction of waste, this philosophy provides reduction in costs as well as gains in productivity and quality. In 2016, P3E has made it possible to improve the efficiency of Commercial Aviation, through a project aimed at reducing production cycles. The program also resulted in the qualification of the sales process for Executive Aviation, which is generating better operating margins.

Brazil’s Most Innovative Company | Award from the Valor Econômico newspaper, in partnership with the consulting firm Strategy&. The company came in first place in the ranking based on an evaluation of the revenues invested in innovation, the creation of new products and the maturity of innovation processes.
2016 Best Companies to Work For in Brazil | Ranking shared by the consulting firm Great Place to Work® and by the magazine Época. This recognition demonstrates the culture of valuing the internal public and its commitment to the company’s performance.
The Best Companies for Starting your Career | Survey conducted by the magazine Você S/A in partnership with the Fundação Instituto de Administração (FIA) and Companhia de Talentos, which evaluates the satisfaction of young people starting their careers.
Best Companies for Human Resources | Award given by the newspaper Valor Econômico and by the consulting firm Aon to companies that adopt the best practices in human resources management.
Transparency in Corporate Reports: Evaluating Multinationals in Emerging Markets | Study conducted by the International Transparency NGO, which analyzed 100 companies operating in 185 markets and headquartered in 15 countries. Among the 12 Brazilian companies analyzed, Embraer was the only one to be graded above 5 (5.6) on a scale from zero (least transparent company) to 10 (most transparent company).
Empresas Mais | Prize given by the newspaper O Estado de S. Paulo in partnership with the Fundação Instituto de Administração (FIA). Embraer won first place for the category “Vehicles and Car Parts” and stood out among the ten leaders in Corporate Governance.
Aviation International News’ 2016 Product Support Survey | Product support survey conducted annually by the U.S. magazine Aviation International News (AIN). In 2016, Embraer’s Executive Aviation reached the top of the ranking with the highest average for all aspects of the survey (8.4 points out of a total of 10) for new and used executive jets.
Pro Pilot magazine’s Corporate Aircraft Product Support Survey | Executive Aviation also stood out by taking first place, for the second consecutive year, in the customer support survey for executive aircraft from the magazine Pro Pilot. Embraer achieved 8.58 points, the highest score among all manufacturers in the 26 years that the survey has been conducted.
1. Function exercised in compliance with American law, especially the Sarbanes-Oxley Act.
2. Except in countries whose laws do not allow reports to be made anonymously. In this case, Embraer abides by local legislation.